Securing Operational Technology For Manufacturing
Manufacturing spans many different industries including metals, machinery, electrical equipment, and transportation equipment. The expansive nature of the industry and its critical role in supply chain and infrastructure support makes it a key target of ransomware and other cybersecurity attacks
Cyber Attacks on the Manufacturing Industry
- Manufacturing was the most targeted industry in 2021, with 23% reporting ransomware attacks (IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index)
- Slowdowns and operational downtime pressure downstream supply chains into ransom payments
- Popular attack methods include phishing and vulnerability exploitation
- Sixty-one percent of incidents at OT-connected organizations last year were in the manufacturing industry
Ransomware Risks Halting Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies often rely on highly interconnected, automated, and complex systems to run machinery and computers for their operations. Any type of cybersecurity attack that spreads throughout their network can potentially bring operations to a halt and result in costly breaches and downtime.
Ransomware attacks not only disrupt and stop operations, they can also result in the leakage of intellectual property, as modern ransomware attacks often involve both extortion and the stealing of data.
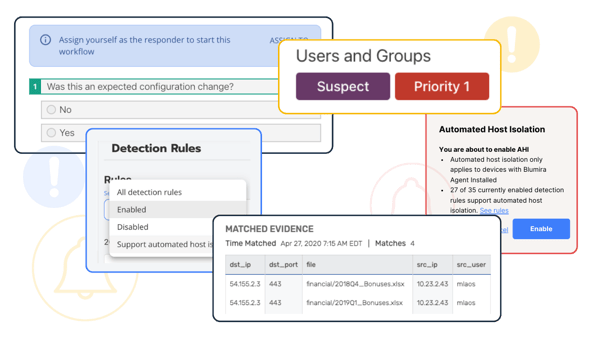
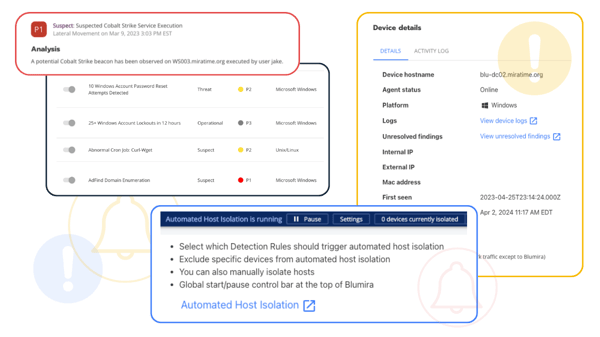
Blumira SIEM + XDR For Manufacturing
Blumira is an easy, effective XDR platform that helps manufacturing companies secure their operational technology with:

Atlantic Constructors, Inc. (ACI)
Challenge – The IT Director of Atlantic Constructors, Inc. (ACI) needed a simplified SIEM that his small IT team could use to keep their organization safe from ransomware and account takeovers.
Solution – ACI turned to Blumira cloud SIEM to help them detect previously unknown threats, following response playbooks written for IT teams to help them remediate threats quickly and easily.
Learn MoreISO 27001: Manufacturing Compliance
Complying with ISO 27001 verifies an organization has a system in place to handle risks related to the security of data owned or handled by the company. Blumira helps manufacturers and service providers protect against operational disruptions and business downtime, as well as supporting many ISO 27001 controls.
-
Access Controls: A.9
Access Controls: A.9
- A.9.2 User access management – Objective: To ensure authorized user access and to prevent unauthorized access to systems and services.
- A.9.2.1 User registration and de-registration – A formal user registration and de-registration process shall be implemented to enable assignment of access rights.
- A.9.3.1 Use of secret authentication information – Users shall be required to follow the organization’s practices in the use of secret authentication information.
- A.9.4 System and application access control – Objective: To prevent unauthorized access to systems and applications.
- A.9.4.1 Information access restriction – Access to information and application system functions shall be restricted in accordance with the access control policy.
- A.9.4.2 Secure log-on procedures – Where required by the access control policy, access to systems and applications shall be controlled by a secure log-on procedure.
- A.9.4.4 Use of privileged utility programs – The use of utility programs that might be capable of overriding system and application controls shall be restricted and tightly controlled.
- A.9.4.5 Access control to program source code – Access to program source code shall be restricted.
-
Protection From Malware; Logging and Monitoring: A.12.2 & A12.4
Protection From Malware; Logging and Monitoring: A.12.2 & A12.4
- A.12.2.1 Controls against malware – Detection, prevention and recovery controls to protect against malware shall be implemented, combined with appropriate user awareness.
- A.12.4.1 Event logging – Event logs recording user activities, exceptions, faults and information security events shall be produced, kept, and regularly reviewed.
- A.12.4.2 Protection of log information – Logging facilities and log information shall be protected against tampering and unauthorized access.
- A.12.4.3 Administrator and operator logs – System administrator and system operator activities shall be logged and the logs protected and regularly reviewed.
- A.12.4.4 Clock synchronization – The clocks of all relevant information processing systems within an organization or security domain shall be synchronized to a single reference time source.
-
Communications Security: A.13
CusCommunications Security: A.13 tomized Search Results
- A.13.1.1 Network controls – Networks shall be managed and controlled to protect information in systems and applications.
- A.13.2.1 Information transfer policies and procedures – Formal transfer policies, procedures and controls shall be in place to protect the transfer of information through the use of all types of communication facilities.
- A.13.2.3 Electronic messaging – Information involved in electronic messaging shall be appropriately protected.
-
Information Security Incident Management: A.16
Information Security Incident Management: A.16
- A.16.1 Management of information security incidents and improvements – Objective: To ensure a consistent and effective approach to the management of information security incidents, including communication on security events and weaknesses
- A.16.1.1 Responsibilities and Procedures – Management responsibilities and procedures shall be established to ensure a quick, effective and orderly response to information security incidents.
- A.16.1.2 Reporting information security events – Information security events shall be reported through appropriate management channels as quickly as possible.
- A.16.1.5 Response to information security incidents — Information security incidents shall be responded to in accordance with the documented procedures.
- A.16.1.6 Learning from information security incidents – Knowledge gained from analyzing and resolving information security incidents shall be responded to in accordance with the documented procedures.
- A.16.1.7 Collection of evidence – The organization shall define and apply procedures for the identification, collection, acquisition, and preservation of information, which can serve as evidence.
-
Compliance: A.18
Compliance: A.18
- A.18.1 Compliance with legal and contractual requirements – Objective: To avoid breaches of legal, statutory, regulatory, or contractual obligations related to information security and of any security requirements.
- A.18.1.3 Protection of records – Records shall be protected from loss, destruction, falsification, unauthorized access and unauthorized release, in accordance with legislators, regulatory, contractual and business requirements.
Access Controls: A.9
- A.9.2 User access management – Objective: To ensure authorized user access and to prevent unauthorized access to systems and services.
- A.9.2.1 User registration and de-registration – A formal user registration and de-registration process shall be implemented to enable assignment of access rights.
- A.9.3.1 Use of secret authentication information – Users shall be required to follow the organization’s practices in the use of secret authentication information.
- A.9.4 System and application access control – Objective: To prevent unauthorized access to systems and applications.
- A.9.4.1 Information access restriction – Access to information and application system functions shall be restricted in accordance with the access control policy.
- A.9.4.2 Secure log-on procedures – Where required by the access control policy, access to systems and applications shall be controlled by a secure log-on procedure.
- A.9.4.4 Use of privileged utility programs – The use of utility programs that might be capable of overriding system and application controls shall be restricted and tightly controlled.
- A.9.4.5 Access control to program source code – Access to program source code shall be restricted.
Protection From Malware; Logging and Monitoring: A.12.2 & A12.4
- A.12.2.1 Controls against malware – Detection, prevention and recovery controls to protect against malware shall be implemented, combined with appropriate user awareness.
- A.12.4.1 Event logging – Event logs recording user activities, exceptions, faults and information security events shall be produced, kept, and regularly reviewed.
- A.12.4.2 Protection of log information – Logging facilities and log information shall be protected against tampering and unauthorized access.
- A.12.4.3 Administrator and operator logs – System administrator and system operator activities shall be logged and the logs protected and regularly reviewed.
- A.12.4.4 Clock synchronization – The clocks of all relevant information processing systems within an organization or security domain shall be synchronized to a single reference time source.
![]() CusCommunications Security: A.13 tomized Search Results
CusCommunications Security: A.13 tomized Search Results
- A.13.1.1 Network controls – Networks shall be managed and controlled to protect information in systems and applications.
- A.13.2.1 Information transfer policies and procedures – Formal transfer policies, procedures and controls shall be in place to protect the transfer of information through the use of all types of communication facilities.
- A.13.2.3 Electronic messaging – Information involved in electronic messaging shall be appropriately protected.
![]() Information Security Incident Management: A.16
Information Security Incident Management: A.16
- A.16.1 Management of information security incidents and improvements – Objective: To ensure a consistent and effective approach to the management of information security incidents, including communication on security events and weaknesses
- A.16.1.1 Responsibilities and Procedures – Management responsibilities and procedures shall be established to ensure a quick, effective and orderly response to information security incidents.
- A.16.1.2 Reporting information security events – Information security events shall be reported through appropriate management channels as quickly as possible.
- A.16.1.5 Response to information security incidents — Information security incidents shall be responded to in accordance with the documented procedures.
- A.16.1.6 Learning from information security incidents – Knowledge gained from analyzing and resolving information security incidents shall be responded to in accordance with the documented procedures.
- A.16.1.7 Collection of evidence – The organization shall define and apply procedures for the identification, collection, acquisition, and preservation of information, which can serve as evidence.
Compliance: A.18
- A.18.1 Compliance with legal and contractual requirements – Objective: To avoid breaches of legal, statutory, regulatory, or contractual obligations related to information security and of any security requirements.
- A.18.1.3 Protection of records – Records shall be protected from loss, destruction, falsification, unauthorized access and unauthorized release, in accordance with legislators, regulatory, contractual and business requirements.
Additional Security Resources
View All
Customer Story: Mid-Sized Manufacturing Firm
Read MoreHow Manufacturers Can Secure Themselves Against Cyber Threats
Read More
Four Cornerstones Of Cyber Resilience In Modern Manufacturing
Read MoreGet Started for Free
Experience the Blumira Free SIEM, with automated detection and response plus compliance reports for 3 cloud connectors, forever.