FTC Safeguards Rule Compliance
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Safeguards Rule, or Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information, was updated in early 2022 to require all non-banking financial institutions – such as mortgage brokers, auto dealerships, and others – develop, implement, and maintain a comprehensive cybersecurity system to keep customer information safe. The Safeguards Rule amendments require organizations within scope of compliance to implement technology for audit trails and to monitor all unauthorized activity. The purpose of the Safeguards Rule, like most FTC regulations, is consumer protection and data security. The original Safeguards Rule took effect in 2003; however, the 2021 amendment ensures that institutions are keeping pace with current technology to keep consumers’ financial information safe.
Who Is Affected By The FTC Safeguards Rule?
The FTC defines a financial institution as “any institution the business of which is engaging in an activity that is financial in nature or incidental to such financial activities as described in section 4(k) of the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956.” According to the FTC, financial institutions are not subject to the enforcement authority of another regulator under section 505 of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA).
What’s new to the inclusion of financial services is the concept of finders: companies that bring together buyers and sellers to negotiate and complete the transaction.
- Accountants & professional tax preparers
- Automotive dealerships that lease vehicles
- Career counselors of individuals in financial industries
- Check printers
- Check-cashing businesses
- Courier services
- Credit reporting agencies.
- Investment advisory company
- Mortgage brokers
- Nonbank lenders
- Payday lenders
- Personal property or real estate appraisers
- Real estate settlement services
- Retailers that extend their own credit
- Wire transfer businesses
How Blumira Helps With FTC Compliance
See our compliance checklist for guidance on how to implement a comprehensive security system to meet FTC requirements.
FTC Requirement for Audit Trails
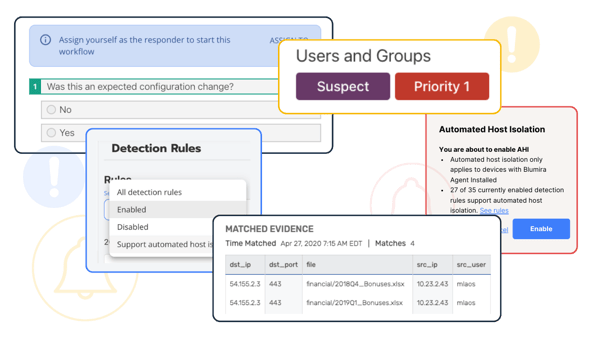
The FTC believes logging user activity is a crucial component of information security because in the event of a security event it allows financial institutions to understand what was accessed and when. Audit trails are chronological logs that show who has accessed an information system and what activities the user engaged in during a given period. Financial institutions are expected to use logging to “monitor” active users and reconstruct past events.
Blumira provides small and medium-sized businesses with an easy and fast all-in-one SIEM solution that combines logging with detection and response. Small teams can deploy the solution within hours to help satisfy FTC requirements. Blumira provides:
- Up to one year of log data retention (audit trails), with immediate availability to help with investigation and incident response.
- Unauthorized activity monitoring to help identify attacker behavior with real-time automated detection under 50 seconds and guided playbooks to help you respond to threats faster.
- Access to our security team to help with guided response, available 24/7 for urgent priority issues.
FTC Compliance Updates at a Glance
The Safeguards Rule amendments require organizations within scope of compliance to implement technology for audit trails and to monitor all unauthorized activity.The revised deadline for complying with some of the updated requirements of the Safeguards Rule went into effect on June 9, 2023, with penalties at $45k per violation.
-
Part 1: Required Policies
Part 1: Required Policies
Designated Qualified Individual – An individual on the IT/security team who oversees the information security program.
Incident Response Plan – Your written incident response plan details a series of actions that the security team must take in the event of a cyber incident.
Customer Information Access Controls, Disposal Plan & Change Management – Information access controls restrict who can make changes and creates an audit trail of all changes to help detect unauthorized access.
Oversee Service Providers & Apps – Review the applications you use and vendors that you share data with. If they are also handling financial data, they too must comply with all of these safeguards.
-
Part 2: Reports & Documentation
Part 2: Reports & Documentation
Data & Systems Inventory – The FTC requires you to have an inventory of all data you have stored and the systems they’re on, including customer records, financial records where they are stored, and all the software that they touch.
Risk Assessment – This process will vary for every organization, but at a high level it involves identifying threats to an environment, both internal and external, to the security, confidentiality, and integrity of customer information. This written risk assessment must include criteria for evaluating those risks and threats.
Information Security Program – Use this checklist to build out your information security program. Developing one is an ongoing process that requires an understanding and consideration of the different facets of security described here, documented all together in one program.
Report To Your Board of Directors – Your Qualified Individual must give an update to your Board of Directors (or another governing body such as a Senior Officer if there isn’t a board) on a regular basis, at least once a year.
-
Part 3: Technical Requirements
Part 3: Technical Requirements
Data Encryption – Encrypt customer information on your system and when it’s in transit. If it’s not feasible to use encryption, secure it by using effective alternative controls approved by the Qualified Individual who supervises your information security program.
Multi-Factor Authentication – Enable multi-factor authentication on all systems that employees and contractors log into. MFA is an easy way to add another layer of verification of a user’s identity and prevent the success of attacks like phishing, stolen credentials, and account takeovers
Penetration Testing & Vulnerability Assessments – Penetration testing, vulnerability assessments and continuous monitoring all help to detect both actual and attempted attacks. Continuous monitoring is an excellent way to test your environment.
Monitor and Log Authorized & Suspicious Activity – Implement a solution to monitor when authorized users are accessing customer information on your system and to detect unauthorized or suspicious access.
-
Part 4: Training Requirements
Part 4: Training Requirements
Employee Security Awareness Training – Provide your people with security awareness training and schedule regular refreshers.
Training & Security Updates For Security Personnel – Provide specialized training for employees, affiliates, or service providers who are hands-on with your information security program and verify that they’re monitoring the latest word on emerging threats and countermeasures.
Part 1: Required Policies
Designated Qualified Individual – An individual on the IT/security team who oversees the information security program.
Incident Response Plan – Your written incident response plan details a series of actions that the security team must take in the event of a cyber incident.
Customer Information Access Controls, Disposal Plan & Change Management – Information access controls restrict who can make changes and creates an audit trail of all changes to help detect unauthorized access.
Oversee Service Providers & Apps – Review the applications you use and vendors that you share data with. If they are also handling financial data, they too must comply with all of these safeguards.
Part 2: Reports & Documentation
Data & Systems Inventory – The FTC requires you to have an inventory of all data you have stored and the systems they’re on, including customer records, financial records where they are stored, and all the software that they touch.
Risk Assessment – This process will vary for every organization, but at a high level it involves identifying threats to an environment, both internal and external, to the security, confidentiality, and integrity of customer information. This written risk assessment must include criteria for evaluating those risks and threats.
Information Security Program – Use this checklist to build out your information security program. Developing one is an ongoing process that requires an understanding and consideration of the different facets of security described here, documented all together in one program.
Report To Your Board of Directors – Your Qualified Individual must give an update to your Board of Directors (or another governing body such as a Senior Officer if there isn’t a board) on a regular basis, at least once a year.
Part 3: Technical Requirements
Data Encryption – Encrypt customer information on your system and when it’s in transit. If it’s not feasible to use encryption, secure it by using effective alternative controls approved by the Qualified Individual who supervises your information security program.
Multi-Factor Authentication – Enable multi-factor authentication on all systems that employees and contractors log into. MFA is an easy way to add another layer of verification of a user’s identity and prevent the success of attacks like phishing, stolen credentials, and account takeovers
Penetration Testing & Vulnerability Assessments – Penetration testing, vulnerability assessments and continuous monitoring all help to detect both actual and attempted attacks. Continuous monitoring is an excellent way to test your environment.
Monitor and Log Authorized & Suspicious Activity – Implement a solution to monitor when authorized users are accessing customer information on your system and to detect unauthorized or suspicious access.
Part 4: Training Requirements
Employee Security Awareness Training – Provide your people with security awareness training and schedule regular refreshers.
Training & Security Updates For Security Personnel – Provide specialized training for employees, affiliates, or service providers who are hands-on with your information security program and verify that they’re monitoring the latest word on emerging threats and countermeasures.
Blumira Features to Satisfy FTC Requirements
Blumira provides small and medium-sized businesses with an easy and fast all-in-one SIEM solution that combines logging with detection and response. Small teams can deploy the solution within hours to help satisfy FTC requirements.
Additional Compliance Resources
View more
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Implementation for Mid-Market Companies: 2025 Update
Read MoreVideo - Security Monitoring Essentials for 2025 Compliance
Read MoreMeeting Florida's 2025 Cybersecurity Deadline: Funding and Compliance
Read MoreGet Started for Free
Experience the Blumira Free SIEM, with automated detection and response and compliance reports for 3 cloud connectors, forever.